A new phishing campaign has been observed leveraging a novel loader malware to deliver an information stealer and keylogger called Agent Tesla.
Trustwave SpiderLabs said it identified a phishing email bearing this attack chain on March 8, 2024. The message masquerades as a bank payment notification, urging the user to open an archive file attachment.
The archive (“Bank Handlowy w Warszawie – dowód wpłaty_pdf.tar.gz”) conceals a malicious loader that activates the procedure to deploy Agent Tesla on the compromised host.
“This loader then used obfuscation to evade detection and leveraged polymorphic behavior with complex decryption methods,” security researcher Bernard Bautista said in a Tuesday analysis.
“The loader also exhibited the capability to bypass antivirus defenses and retrieved its payload using specific URLs and user agents leveraging proxies to further obfuscate traffic.”
The tactic of embedding malware within seemingly benign files is a tactic that has been repeatedly employed by threat actors to trick unsuspecting victims into triggering the infection sequence.
The loader used in the attack is written in .NET, with Trustwave discovering two distinct variants that each make use of a different decryption routine to access its configuration and ultimately retrieve the XOR-encoded Agent Tesla payload from a remote server.
In an effort to evade detection, the loader is also designed to bypass the Windows Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI), which offers the ability for security software to scan files, memory, and other data for threats.
It achieves this by “patching the AmsiScanBuffer function to evade malware scanning of in-memory content,” Bautista explained.
The last phase involves decoding and executing Agent Tesla in memory, allowing the threat actors to stealthily exfiltrate sensitive data via SMTP using a compromised email account associated with a legitimate security system supplier in Turkey (“merve@temikan[.]com[.]tr”).
The approach, Trustwave said, not only does not raise any red flags, but also affords a layer of anonymity that makes it harder to trace the attack back to the adversary, not to mention save the effort of having to set up dedicated exfiltration channels.
“[The loader] employs methods like patching to bypass Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) detection and dynamically load payloads, ensuring stealthy execution and minimizing traces on disk,” Bautista said. “This loader marks a notable evolution in the deployment tactics of Agent Tesla.”
The disclosure comes as BlueVoyant uncovered another phishing activity conducted by a cybercrime group called TA544 that leverages PDFs dressed up as legal invoices to propagate WikiLoader (aka WailingCrab) and establish connections with command-and-control (C2) server that almost exclusively encompasses hacked WordPress sites.
It’s worth noting that TA544 also weaponized a Windows security bypass flaw tracked as CVE-2023-36025 in November 2023 to distribute Remcos RAT via a different loader family dubbed IDAT Loader, allowing it to seize control of infected systems.
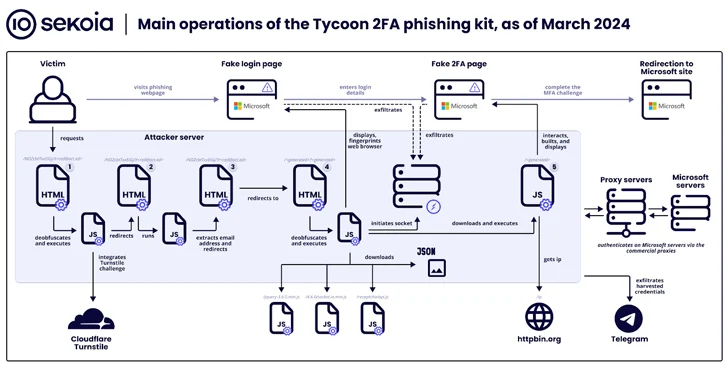
The findings also follow a surge in the use of a phishing kit called Tycoon, which Sekoia said has “become one of the most widespread [adversary-in-the-middle] phishing kits over the last few months, with more than 1,100 domain names detected between late October 2023 and late February 2024.”
Tycoon, publicly documented by Trustwave last month, permits cyber criminals to target users of Microsoft 365 with phony login pages to capture their credentials, session cookies, and two-factor authentication (2FA) codes. It’s known to be active since at least August 2023, with the service offered via private Telegram channels.
The phishing kit is notable for incorporating extensive traffic filtering methods to thwart bot activity and analysis attempts, requiring site visitors to complete a Cloudflare Turnstile challenge before redirecting users to a credential harvesting page.
Tycoon also shares operational and design-level similarities with the Dadsec OTT phishing kit, raising the possibility that the developers had access to and tweaked the source code of the latter to suit their needs. This is supported by the fact that Dadsec OTT had its source code leaked in October 2023.
“The developer enhanced stealth capabilities in the most recent version of the phishing kit,” Sekoia said. “The recent updates could reduce the detection rate by security products of the Tycoon 2FA phishing pages and the infrastructure. Additionally, its ease of use and its relatively low price make it quite popular among threat actors.”